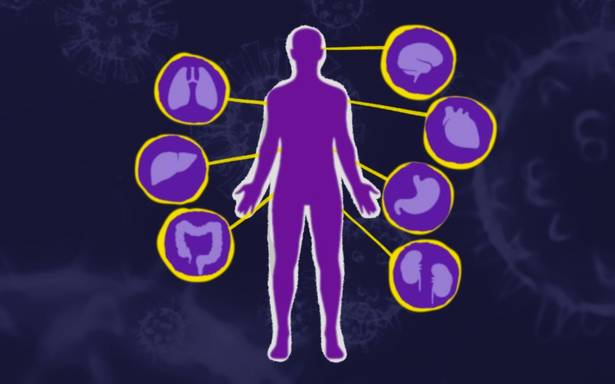
COVID-19 is an infectious disease that was caused by a novel coronavirus. This virus was first identified in Wuhan City, China in December 2019 and has since caused a global pandemic. In September 2020, more than 29 million people in 188 countries were affected by this virus. People affected by it will likely have common symptoms such as fever, cough and shortness of breath. Scientists around the world have come to a conclusion that this virus can cause multi-organ disease, which means that it affects not just a single organ. In this article, we will discuss which organs are most affected by COVID-19.
COVID-19 spreads mainly through air droplets that form when we cough or sneeze. These droplets will be inhaled by another person, and this is how the virus starts entering our body. The first place that they will visit is the lungs, hence becoming the most affected organ by COVID-19. Why is that so? Scientists found out that this virus has an affinity towards an enzyme called ACE2 (Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2). Unsurprisingly, the organ that has an abundance of ACE2 is the lungs. COVID-19 will enter the lungs by binding to the ACE2 receptors that act as the entry point for this virus. It then enters the alveoli, tiny air sacs that are responsible for the exchange of air between the lungs and blood vessels. Our immune system then will start fighting against these viruses and as a result, this disrupts the transfer of oxygen into the lungs. This explains why most patients will have symptoms of breathing difficulty.
Some research that was done in China, Italy and the United States show that COVID-19 also affects the heart. This happens due to the same reason why it affects the lungs. It is found out that the heart contains ACE2 receptors as well. This means that the virus will go to the heart, bind to ACE2 receptors and enter the cells. Statistics show that the number of COVID-19 patients that died from pulmonary and cardiovascular disease such as acute heart injury or heart failure is higher than other causes. It is understood that a biomarker that was released from a damaged heart can be found in these patient’s blood. This means that there is a significant damage done to the heart by the effect of COVID-19. However, it is still not clear whether this virus caused direct damage to the heart or the damage was done due to the reaction towards heart’s infection.
The virus also can affect the brain. This is because the ACE2 receptors are present in the brain tissue. 80% of COVID-19 patients reported an impaired sense of smell and taste. These usually happen at the beginning of infection, and these symptoms may be an early diagnosis of COVID-19. Some patients may develop meningitis and encephalitis, indicating an infection in the neurological system.
Data from Wuhan shows that 6% of COVID-19 patients died from kidney failure. Although this organ is rarely involved, it was proven that the virus will damage the kidney once they infect it. Once again, ACE2 receptor plays the main role. They are present in the kidneys, thus making it vulnerable to the virus. Damage to the kidneys is both caused by the virus itself and the reaction from the immune system. Patients with pre-existing kidney disease are shown to become more susceptible to this infection.
Now we know that if someone is infected with COVID-19, their organs will be susceptible to injury caused by this virus. Organs that are mostly damaged include lungs, heart, brain and kidneys. In some cases, other organs such as the skin, eyes, noses, liver and intestines are also reported to be affected. Hence, we can agree that this multi-organ disease is very dangerous and should be treated with care.