Compression Garments: Choose As Per Your Requirements
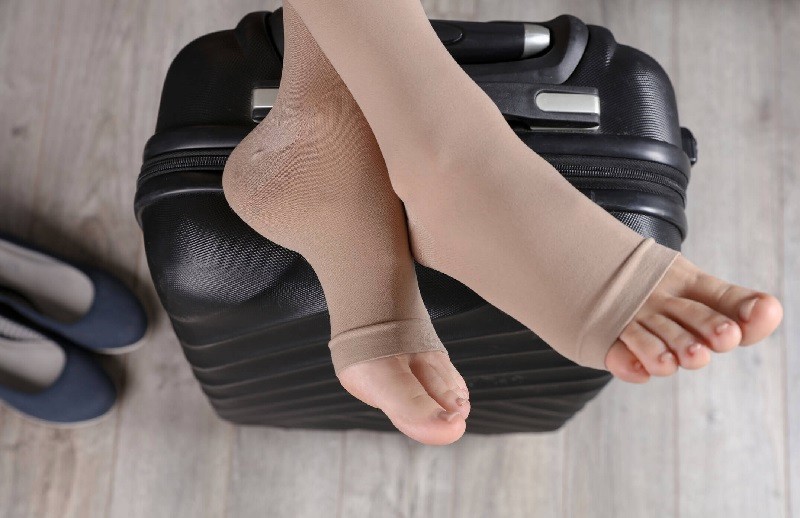

The human being is becoming increasingly sedentary. It is now typical for people to sit for several hours a day, which has a bad impact on their blood circulation system. However, there are treatments and preventative measures available, such as compression clothing.
To ensure that all of the critical organs receive an adequate supply of oxygen supplied by the blood, the human body must move. Sedentary lifestyles can thus produce a variety of difficulties with blood circulation in some persons. A sedentary lifestyle, as well as genetics, lifestyle, and excess weight, can all influence the onset of disorders associated with impaired blood circulation. According to some estimates, venous insufficiency affects more than half of the population (including men and women). Wearing compression clothing can help prevent and, in certain situations, treat circulatory system problems.
Compression garments have numerous applications.
The compression garment, also known as compression garments, applies pressure on the veins, allowing blood to flow more freely to the heart. Compression garments are used to prevent the formation of varicose and spider veins on the legs and thighs in cases of venous insufficiency. Sclerotherapy treatments (a phlebology treatment technique) reduce the risk of venous thrombosis or phlebitis. They also help pregnant women avoid pressure dips, varicose veins, and leg swelling.
Wearing compression clothes promotes healing and improves scar appearance in severe burns and to avoid rigid, shapeless scars. Athletes also frequently use compression clothing because it supports the muscles and aids recovery by increasing oxygenation.
By preventing swelling, the compression garment can also be of considerable assistance in situations of lymphedema. Primary lymphedema, a lymphatic system illness that occurs from birth, produces spontaneous swelling of a limb. Secondary lymphedema can develop after surgery that involves the excision of lymph nodes in the armpits or groyne.
Compression garments for lymphedema are also highly suggested for long-distance travel by plane or car. Confinement in a small space, immobilisation for long periods of time, dehydration, or low pressure at altitude are all risk factors for venous thrombosis.
How to Pick the Right Compression Garment?
A compression garment’s type, size, and compression grade will differ from person to person. Because there are so many items on the market, it is best to consult a healthcare professional, such as a phlebologist or orthotist, before purchasing this type of clothing. The phlebologist is an expert in varicose disorders as well as the treatment of varicose and spider veins. The orthotist (orthotist-prosthetist) can do a biomechanical assessment, as well as fabricate and adjust any orthopaedic device (foot orthosis, orthopaedic orthosis, orthopaedic prosthesis, compression garment, walking aid, and wheelchair).
Conclusion
Compression garments are expected to have an impact on performance and recuperation via physiological, mechanical, and psychological factors.
However, in many circumstances, the results are insufficient to substantiate these ostensible benefits. Overall, the benefits of wearing compression garments are larger during high-intensity, repeated exercise, such as sprints or chain leaps, than during endurance exercises.
The effects of compression appear to be greatest when used as a healing method for 24 to 48 hours following exercise that causes muscle injury.